neoplasia in cats lungs
Primary pulmonary neoplasia is less common than metastatic neoplasia in dogs and cats. Primary lung tumors are cancers that arise in the lung tissue of both dogs and cats.

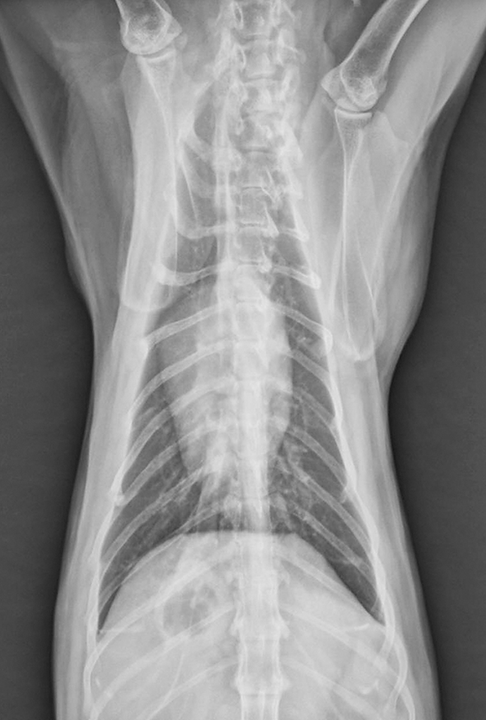
Radiographic And Macroscopic Findings In 3 Cats With Idiopathic Download Scientific Diagram
The goal of this article is to describe the common histologic variants clinical signs biologic behavior and newest options for early diagnosis and effective treatment of primary lung tumors in dogs and cats.
. Neoplasia is the term for various types of abnormal growths caused by the uncontrolled division of cells. The most common type of tumor of the lungs is a pulmonary carcinoma. Primary pulmonary neoplasia in cats.
Cancer also called neoplasia presents in many different often nonspecific ways in cats. Carcinomas are malignant tumors that develop from the epithelial tissues in the lungs. Lethargy wheezing vomiting fever or lameness may also be seen.
However when cats do develop tumours they are much more likely to be malignant 3-4 times more likely than in dogs and therefore much more likely to cause serious. Although primary pulmonary neoplasms are rare findings in dogs and cats the. Cats with preoperative lymph node enlargement and pleural effusion have shorter survival times than cats without.
With a preoperative computed tomography scan that influence survival of cats undergoing surgical removal of a primary lung tumour. Feline Metastatic Neoplasia Cancer Metastatic neoplasia commonly referred to as mets is cancer that has spread from its original site to other sites in the body. The lungs and local lymph nodes are common sites of metastasis for many tumor types but metastases can occur in almost any organ and are associated with malignant tumors in cats.
The diaphragmatic lobes are most frequently involved with the right lung lobes more often affected than the left. Overall cats suffer with neoplasia or development of tumours less frequently than dogs. While cancer is usually diagnosed in senior cats certain cancers can develop in cats of any age.
Veterinary Medicine Biomedical Sciences Texas AM University College Station TX USA. Regional lymph node involvement in 29-35 and distant metastasis in 46-58. This article covers the pertinent clinical physical and radiographic findings in dogs and cats with primary pulmonary neoplasia.
Primary pulmonary neoplasia is rare in cats with a reported annual incidence in one study of 22 per 100 000 cats 22 while a further study reported an incidence of pulmonary neoplasia of 038 of cats examined at necropsy. Pulmonary Neoplasia - WSAVA2013 - VIN. Specific anatomic localization of tumor origin is not always possible and more than one tumor type may be present.
Chest x-rays are the first step in making a diagnosis. Most dogs and cats with pulmonary neoplasia are middle-aged or geriatric 23. However a definitive diagnosis of lung cancer requires a sample of tissue biopsy.
Specific anatomic localization of tumor origin is not always possible and more. Most lung tumors in cats are found after a prolonged incubation period. Overview of Lung Cancer in Cats.
They are rare in both species but slightly more common in dogs. Metastasis to multiple digits presenting as swelling of 1 toes and lameness without respiratory signs is a common primary complaint. In cases with more advanced stages of lung cancer breathing difficulties excessive coughing and exercise intolerance are often observed.
For this reason more cats with pulmonary tumors present with paraneoplastic syndromes than present with signs associated with the primary tumor Feline cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes. Other types of tumors can develop in the lungs but these are the result of metastasis spread from a tumor elsewhere in the body and are not considered to be primary lung tumors. Diagnosis is usually established based on radiographs cytologic examination.
An update on diagnosing and treating primary lung tumors. Early detection and surgical treatment of carefully selected cases can. The diaphragmatic lobes are most frequently involved with the right lung lobes more often affected than the left.
Carcinomas are malignant tumors that develop from the epithelial tissues in the lungs. Generalized signs of illness such as fever vomiting decrease in appetite. Primary lung tumors are cancers that arise in the lung tissue of both dogs and cats.
Overview of Lung Cancer in Cats. The most common type of tumor is a carcinoma. There are many different forms of cancer and since the symptoms are so varied any lumps or bumps wounds that dont heal changes in behavior including appetite weight litter box.
Distant metastatic sites include pleural cavity in 65 and extrathoracic sites in 35. 23 Affected cats are generally middle to old-aged and tumor development is independent of feline. They are rare in both species but slightly more common in dogs.
Assessment of computed tomography findings and survival. Cats usually do not demonstrate altered respiratory patterns until disease is very advanced. Primary pulmonary neoplasia.
They may live longer and divide faster. Dogs and cats with early-stage lung cancer are usually asymptomatic or present with very mild symptoms such as occasional coughing. Primary pulmonary neoplasia is less common than metastatic neoplasia in dogs and cats.
Squamous cell carcinoma and bronchioalveolar carcinoma are other types of cancer that occur in cat lungs. The most common type of tumor is a carcinoma. Neoplasms may perhaps be seen less than half as frequently in cats compared with dogs.
In a retrospective study by Smith and colleagues of 127 cats with ATE neoplasia was the second most common cause of feline ATE after myocardial disease occurring in 6 of cases 17 and pulmonary carcinoma was the commonest neoplastic condition. Primary pulmonary tumors are rare in both dogs and cats. Presenting signs can include cough exercise intolerance dyspnea lameness from metastasis or hypertrophic pulmonary osteopathy the latter more common in dogs than in cats weight loss anorexia and lethargy 238.
Fluid accumulation around the lungs called pleural effusion is common in cats with primary lung tumors. These rogue cells called neoplastic cells do not behave and are not controlled like normal cells. 75 metastatic rate for primary lung tumors in cats.
Diagnostic and treatment recommendations are made. 61819 The literature suggests that acute onset of hindlimb ischaemia occurs as the primary presenting. The most common primary lung tumour in cats is pulmonary adenocarcinoma which can arise from the bronchus the tubes that carry air into the lungs or from the alveolae the air sacs.
Although primary pulmonary neoplasia is rare in both the dog and cat it appears to be diagnosed with increasing frequency. Cat Diseases Conditions A-Z.
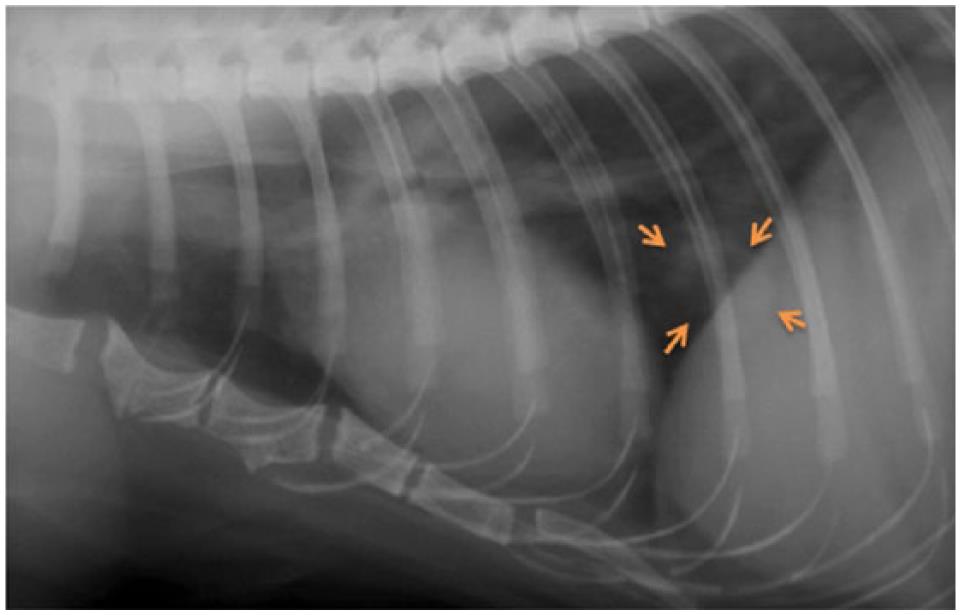
Metastatic Pulmonary Carcinomas In Cats Feline Lung Digit Syndrome Further Variations On A Theme

Pulmonary Neoplasia Digital Metastasis In Cats Clinician S Brief

Macau Daily Times 澳門每日時報 Ask The Vet Lung Cancer In Cats

Lung Cat No 1 Diffuse Severe Bronchointerstitial Pattern Download Scientific Diagram
Lung Cancer In Cats Causes Symptoms Treatment All About Cats

Common Pulmonary Diseases In Cats Clinician S Brief

Important Facts About Your Cat S Body Infographic Dog Health Dog Care Pets

Pulmonary Neoplasia Digital Metastasis In Cats Clinician S Brief
Cancer In Cats Not All Dark Masses Are Cancerous Tumors Cancer In Pets Petmd